VARIETY- DATA
STRUCTURE AND TYPES
What is the
Data Structure
A data
structure is a specialized format for organizing, processing, retrieving and
storing data. There are several basic and advanced types of data structures,
all designed to arrange data to suit a specific purpose. Data structures make
it easy for users to access and work with the data they need in appropriate
ways. Most importantly, data structures frame the organization of information
so that machines and humans can better understand it.
In computer
science and computer programming, a data structure may be selected or designed
to store data for the purpose of using it with various algorithms. In some
cases, the algorithm's basic operations are tightly coupled to the data
structure's design. Each data structure contains information about the data
values, relationships between the data and -- in some cases -- functions that
can be applied to the data.
For
instance, in an object-oriented programming language, the data structure and
its associated methods are bound together as part of a class definition. In
non-object-oriented languages, there may be functions defined to work with the
data structure, but they are not technically part of the data structure.
Why Data
Structure is Important?
Typical
base data types, such as integers or floating-point values, that are available
in most computer programming languages are generally insufficient to capture
the logical intent for data processing and use. Yet applications that ingest,
manipulate and produce information must understand how data should be organized
to simplify processing. Data structures bring together the data elements in a
logical way and facilitate the effective use, persistence and sharing of data.
They provide a formal model that describes the way the data elements are
organized.
Data
structures are the building blocks for more sophisticated applications. They
are designed by composing data elements into a logical unit representing an
abstract data type that has relevance to the algorithm or application. An
example of an abstract data type is a "customer name" that is
composed of the character strings for "first name," "middle
name" and "last name."
Data
Structure Types
The data
structure type used in a particular situation is determined by the type of
operations that will be required or the kinds of algorithms that will be
applied. The various data structure types include the following:
1. Arrays
An array is
a structure of fixed-size, which can hold items of the same data type. It can
be an array of integers, an array of floating-point numbers, an array of
strings or even an array of arrays (such as 2-dimensional arrays). Arrays are
indexed, meaning that random access is possible.
Fig 1. Visualization
of basic Terminology of Arrays (Image by author)
Array operations
Traverse: Go through the elements and print them.
Search: Search for an element in the array. You can
search the element by its value or its index
Update: Update the value of an existing element at a
given index
Inserting
elements to an array and deleting elements from an array cannot be done
straight away as arrays are fixed in size. If you want to insert an element to
an array, first you will have to create a new array with increased size
(current size + 1), copy the existing elements and add the new element. The
same goes for the deletion with a new array of reduced size.
Applications of arrays
Used as the
building blocks to build other data structures such as array lists, heaps, hash
tables, vectors and matrices.
Used for
different sorting algorithms such as insertion sort, quick sort, bubble sort
and merge sort.
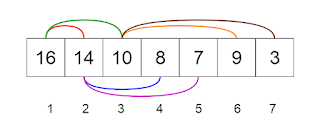
2. Linked Lists
A linked
list is a sequential structure that consists of a sequence of items in linear
order which are linked to each other. Hence, you have to access data
sequentially and random access is not possible. Linked lists provide a simple
and flexible representation of dynamic sets.
Elements in
a linked list are known as nodes.
Each node
contains a key and a pointer to its successor node, known as next.
The
attribute named head points to the first element of the linked list.
The last
element of the linked list is known as the tail.
Fig 2.
Visualization of basic Terminology of Linked Lists (Image by author)
Following
are the various types of linked lists available.
Singly linked list — Traversal of items can be done in the
forward direction only.
Doubly linked list — Traversal of items can be done in both
forward and backward directions. Nodes consist of an additional pointer known
as prev, pointing to the previous node.
Circular linked lists — Linked lists where the prev
pointer of the head points to the tail and the next pointer of the tail points
to the head.
Linked list operations
Search: Find the first element with the key k in the
given linked list by a simple linear search and returns a pointer to this
element
Insert: Insert a key to the linked list. An insertion
can be done in 3 different ways; insert at the beginning of the list, insert at
the end of the list and insert in the middle of the list.
Delete: Removes an element x from a given linked
list. You cannot delete a node by a single step. A deletion can be done in 3
different ways; delete from the beginning of the list, delete from the end of
the list and delete from the middle of the list.
Applications of linked lists
Used for
symbol table management in compiler design.
Used in
switching between programs using Alt + Tab (implemented using Circular Linked
List).
3. Stacks
A stack is
a LIFO (Last In First Out — the element placed at last can be accessed at
first) structure which can be commonly found in many programming languages.
This structure is named as “stack” because it resembles a real-world stack — a
stack of plates.
Stack operations
Given below
are the 2 basic operations that can be performed on a stack. Please refer to
Figure 3 to get a better understanding of the stack operations.
Push:
Insert an element on to the top of the stack.
Pop: Delete
the topmost element and return it.
Fig 3. Visualization
of basic Operations of Stacks (Image by author)
Furthermore,
the following additional functions are provided for a stack in order to check
its status.
Peek: Return the top element of the stack without
deleting it.
Empty: Check if the stack is empty.
Full: Check if the stack is full.
Applications of stacks
Used for
expression evaluation (e.g.: shunting-yard algorithm for parsing and evaluating
mathematical expressions).
Used to
implement function calls in recursion programming.
4. Queues
A queue is
a FIFO (First In First Out — the element placed at first can be accessed at
first) structure which can be commonly found in many programming languages.
This structure is named as “queue” because it resembles a real-world queue —
people waiting in a queue.
Queue operations
Given below
are the 2 basic operations that can be performed on a queue. Please refer to
Figure 4 to get a better understanding of the queue operations.
Enqueue: Insert an element to the end of the queue.
Dequeue: Delete the element from the beginning of the
queue.
Fig 4.
Visualization of Basic Operations of Queues (Image by author)
Applications of queues
Used to
manage threads in multithreading.
Used to
implement queuing systems (e.g.: priority queues).
5. Hash Tables
A Hash
Table is a data structure that stores values which have keys associated with
each of them. Furthermore, it supports lookup efficiently if we know the key
associated with the value. Hence it is very efficient in inserting and
searching, irrespective of the size of the data.
Direct
Addressing uses the one-to-one mapping between the values and keys when storing
in a table. However, there is a problem with this approach when there is a
large number of key-value pairs. The table will be huge with so many records
and may be impractical or even impossible to be stored, given the memory
available on a typical computer. To avoid this issue we use hash tables.
Hash Function
A special
function named as the hash function (h) is used to overcome the aforementioned
problem in direct addressing.
In direct
accessing, a value with key k is stored in the slot k. Using the hash function,
we calculate the index of the table (slot) to which each value goes. The value
calculated using the hash function for a given key is called the hash value
which indicates the index of the table to which the value is mapped.
h(k) = k %
m
h: Hash
function
k: Key of
which the hash value should be determined
m: Size of
the hash table (number of slots available). A prime value that is not close to
an exact power of 2 is a good choice for m.
Fig 5.
Representation of a Hash Function (Image by author)
Consider
the hash function h(k) = k % 20, where the size of the hash table is 20. Given
a set of keys, we want to calculate the hash value of each to determine the
index where it should go in the hash table. Consider we have the following
keys, the hash and the hash table index.
1 → 1%20 →
1
5 → 5%20 →
5
23 → 23%20
→ 3
63 → 63%20
→ 3
From the
last two examples given above, we can see that collision can arise when the
hash function generates the same index for more than one key. We can resolve
collisions by selecting a suitable hash function h and use techniques such as
chaining and open addressing.
Applications of hash tables
Used to
implement database indexes.
Used to
implement associative arrays.
Used to
implement the “set” data structure.
6. Trees
A tree is a
hierarchical structure where data is organized hierarchically and are linked
together. This structure is different from a linked list whereas, in a linked
list, items are linked in a linear order.
Various
types of trees have been developed throughout the past decades, in order to
suit certain applications and meet certain constraints. Some examples are
binary search tree, B tree, treap, red-black tree, splay tree, AVL tree and
n-ary tree.
Binary Search Trees
A binary
search tree (BST), as the name suggests, is a binary tree where data is
organized in a hierarchical structure. This data structure stores values in
sorted order.
Every node
in a binary search tree comprises the following attributes.
key: The
value stored in the node.
left: The
pointer to the left child.
right: The
pointer to the right child.
p: The
pointer to the parent node.
A binary
search tree exhibits a unique property that distinguishes it from other trees.
This property is known as the binary-search-tree property.
Let x be a
node in a binary search tree.
If y is a
node in the left subtree of x, then y.key ≤ x.key
If y is a node in the right subtree of x, then y.key ≥ x.key
Fig 6.
Visualization of Basic Terminology of Trees (Image by author)
Fig 6.
Visualization of Basic Terminology of Trees (Image by author)
Applications of trees
Binary Trees: Used to implement expression parsers and
expression solvers.
Binary Search Tree: used in many search applications where data
are constantly entering and leaving.
Heaps: used by JVM (Java Virtual Machine) to store
Java objects.
Treaps: used in wireless networking.
Check my
articles below on 8 useful tree data structures and self-balancing binary search
trees.
8 Useful
Tree Data Structures Worth Knowing
An overview
of 8 different tree data structures
7. Heaps
A Heap is a
special case of a binary tree where the parent nodes are compared to their
children with their values and are arranged accordingly.
Let us see
how we can represent heaps. Heaps can be represented using trees as well as
arrays. Figures 7 and 8 show how we can represent a binary heap using a binary
tree and an array.
Fig 7.
Binary Tree Representation of a Heap (Image by author)
Fig 8.
Array Representation of a Heap (Image by author)
Heaps can be of 2 types.
Min Heap — the key of the parent is less than or equal
to those of its children. This is called the min-heap property. The root will
contain the minimum value of the heap.
Max Heap — the key of the parent is greater than or
equal to those of its children. This is called the max-heap property. The root
will contain the maximum value of the heap.
Applications of heaps
Used in
heapsort algorithm.
Used to
implement priority queues as the priority values can be ordered according to
the heap property where the heap can be implemented using an array.
Queue
functions can be implemented using heaps within O(log n) time.
Used to
find the kᵗʰ smallest (or largest) value in a given array.
Check my
article below on implementing a heap using the python heapq module.
Introduction
to Python Heapq Module
A simple
introduction on how to use Python’s heapq module
towardsdatascience.com
8. Graphs
A graph
consists of a finite set of vertices or nodes and a set of edges connecting
these vertices.
The order
of a graph is the number of vertices in the graph. The size of a graph is the
number of edges in the graph.
Two nodes
are said to be adjacent if they are connected to each other by the same edge.
Directed Graphs
A graph G
is said to be a directed graph if all its edges have a direction indicating
what is the start vertex and what is the end vertex.
We say that
(u, v) is incident from or leaves vertex u and is incident to or enters vertex
v.
Self-loops:
Edges from a vertex to itself.
Undirected Graphs
A graph G
is said to be an undirected graph if all its edges have no direction. It can go
in both ways between the two vertices.
If a vertex
is not connected to any other node in the graph, it is said to be isolated.
Fig 9.
Visualization of Terminology of Graphs (Image by author)
THE TRAVEL INDUSTRY'S DATA SOLUTION
In contrast
to some business jargon, big data is precisely what it sounds like. Each
airline reservation and hotel stay generates a data trail that is stored in
traditional databases, but we are now generating vast swaths of digital data on
social media, online review sites, search engines, and retail platforms.
Smartphones
have increased the volume: every text, search, call, email, and photo or video
we upload or share is stored, frequently in conjunction with our location.
Globally, the total volume of data held is increasing at an astounding rate,
doubling every 14 months.
The new gold standard is data.
Without a
doubt, you've heard the expression 'data is the new gold.' However, just like
gold, data must be refined and processed in order to retain any value.
How is the
travel industry to make sense of massive amounts of data? As an online travel
agent, tour operator, or wholesaler, you can leverage big data to gain insight
into your competitors and your own online reputation, as well as to optimize
your revenue management and marketing strategy.
Due to the
massive amounts of publicly available big data, it can only be collected and
processed using artificial intelligence. Today, you can choose from a variety
of data analysis firms that specialize in travel-related services and typically
charge a monthly fee. Additionally, there are some free tools available, such
as Google Analytics.
All of this
data can assist you in maintaining competitive pricing and developing dynamic
packaging that works for your customers.
Take notes from your competitors.
Typically,
data analysis companies provide a service via a dashboard that allows you to
view and compare your performance to that of a select number of your
competitors. The data is aggregated from a variety of sources (social media,
online review sites, and search engines) and presented in an easily digestible
format under a series of headings such as sentiment, SEO ratings, reviews,
prices, and strategy.
Greater
business transparency has been achieved as a result of the digital revolution.
Utilize it to the fullest. There is a wealth of information available about
your market and your competitors, and it is all freely accessible. Bear in mind
that you can never truly comprehend your own performance unless you compare it
to that of your competitors.
Take control of your online reputation
On a
variety of online platforms and in a variety of different languages,
individuals may be writing about your company and the services you provide.
Without a mechanism for collecting this feedback, you risk missing out on free
publicity (in the case of positive reviews) or the opportunity to correct a
service failure or misunderstanding (in the case of bad reviews).
At the most
basic level, you can create a Google Alert to monitor whenever your business is
mentioned online; however, monitoring and responding to online mentions can be
hit-or-miss and time-consuming. If your business has grown to the point where
manually monitoring your online reputation is no longer feasible, you will need
to hire a data analysis provider.
Typically,
both your online reputation and that of your competitors are logged and
tracked. However, the primary advantage of such a service is the ability to
directly respond to reviews regardless of their source, all from the same
online platform. Thus, rather than logging into your Facebook, TrustPilot, and
TripAdvisor accounts separately, all of your reviews are consolidated in one
location, and you can view and respond to them all from the same online
dashboard.
Increase your revenue management efficiency
In the
mid-1980s, the airline industry pioneered dynamic pricing with the goal of
selling the right product at the right price to the right customer at the right
time. Although pricing strategies have evolved significantly since then, this
objective remains central to all travel agents' sales and marketing efforts. In
modern times, we also use the look to book ratio to ensure that our sales are
as efficient as possible.
The
significant difference between today and the 1980s is the increased volatility
of price movements. Consider a single instance. A customer makes a hotel
reservation through your platform. The price of that booking will now change an
average of 18 times until check-in time. For you, knowing the optimal time to
re-book that stay at the optimal price point would be extremely beneficial,
resulting in a savings that will directly benefit your bottom line. However,
conventional revenue management techniques are incapable of predicting with
certainty when a price will reach its absolute minimum. And this is where big
data comes in handy. Hotelmize's proprietary algorithm, which is based on 23
million hotel rates worldwide, enables travel companies to increase margins by
up to 30% on bookings already made on their platforms. Additionally, this big
data solution operates in the background, requiring no human intervention.
Hotelmize's big data technology was applied to 280,000 hotel bookings last
year, resulting in a total savings of $15 million, or $53.57 per booking on
average.
Refine and concentrate your marketing efforts
Finally,
intelligent analysis of your own and competitors' digital footprints enables
you to gain a better understanding of your target markets. This enables you to
segment your customers into more specific subgroups and target your marketing
efforts appropriately.
Big data
analytics can be used to forecast demand based on historical performance,
seasonal attractions and events, weather, and public and school holidays.
Additionally, it can identify emerging trends in travel bookings, such as solo
travel, leisure, and digital nomads.
The core
strength of big data is its ability to react quickly and competitively to
predicted changes in travel demand.
Naturally,
the predictive capabilities of big data are limited. Travel is particularly
susceptible to unexpected shocks, such as the current coronavirus outbreak.
Without a doubt, big data can help here as well, hopefully in terms of positive
healthcare and tourism outcomes.
While big
data can be an extremely valuable tool, it should never be used to replace or
suppress your professionalism in overcoming adversity and increasing profit
margins in the tourism industry.
References
1-Loshin,
David(2021)’data structure’,Tech target.
Avaliable at:
https://searchsqlserver.techtarget.com/definition/data-structure
(Accessed: 24 February 2022)
2- Mallawaarachchi, V.(2020)’ 8 Common Data Structures every Programmer must know’,Towards
Data Science. Avaliable at:
https://towardsdatascience.com/8-common-data-structures-every-programmer-must-know-171acf6a1a42 (Accessed: 25 February 2022)
3-Walker,B.(2020)’Big
Data Solutions For Travel Industry’,Hotel Mize. Avaliable at:
https://www.hotelmize.com/blog/big-data-solutions-for-the-travel-industry/
(Accessed:
26 February 2022)
Author: Anil(10598717)
KeyWords:#travel#budget#revolution#social#socialmedia#Data#Industry#BigData#World#Marketing#Extension#Hotel#Tourism#Structure#DataTypes#Data Structure